 |
?
Degenerated RING finger found in protein RMD5 homolog B (RMD5B) RMD5B is one of the vertebrate homologs of yeast Rmd5p. The biological function of RMD5B remains unclear. RMD5B contains a Lissencephaly type-1-like homology motif (LisH), a C-terminal to LisH motif (CTLH) domain, and a degenerated RING finger that is characterized by lacking the second, fifth, and sixth Zn2+ ion-coordinating residues compared with the classic C3H2C3-/C3HC4-type RING fingers. |
|
|
Conserved Features/Sites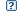
Feature 1: Zn binding site [ion binding site], 4 residue positions
Conserved feature residue pattern:C H C C
Evidence:Comment:The degenerated RING finger is characterized by lacking the second, fifth, and sixth Zn2+ ion-coordinating residues compared with the classic C3H2C3-/C3HC4-type RING fingers, similar to SP-RING fingers. Comment:based on the structures of human Sumo ligases Pias2 and Pias3 with bound Zn2+ ion through their SP-RING fingers Comment:The SP-RING finger is a variant of RING finger; it binds a single Zn ion and lacks the second, fifth, and sixth zinc-binding residues of the consensus C3H2C3-/C3HC4-type RING fingers.
|
|
|
|
|
 |
