
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
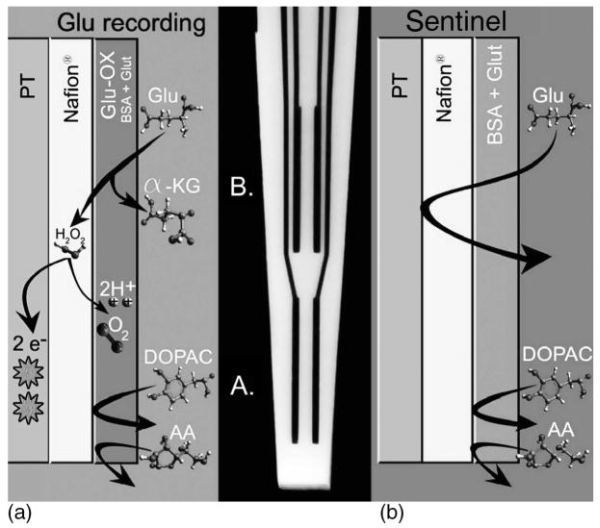
Schematic and photomicrograph of an S2, Nafion coated, self-referencing, L-glutamate selective multisite microelectrode. (a) Schematic showing the bottom pair of Pt recording sites coated with L-glutamate oxidase (Glu-ox), BSA, and glutaraldehyde (Glut). L-glutamate that comes into contact with the Gluox is converted to α-ketoglutarate and peroxide. The peroxide readily diffuses through the Nafion layer that blocks anionic substances such as AA and DOPAC. When the peroxide formed comes into contact with the Pt recording sites at a potential of + 0.7 V versus a Ag/AgCl reference electrode, the peroxide is oxidized and the resulting two electrons are transferred to the Pt recording site and the change in current is measured by the FAST-16 system. (b) Schematic showing the top pair of Pt recording sites coated with the inactive protein matrix of BSA and Glut, also referred to as the sentinel sites. Since no Glu-ox is coated onto this pair of recording sites, L-glutamate is not converted to a reporter molecule and thus is not measured on the Pt recording sites. Once again, the Nafion on these sites repels AA and DOPAC.

NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.