NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012-.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet].
Show detailsOVERVIEW
Introduction
Acrivastine is a second generation antihistamine that is used for the treatment of allergic rhinitis. Acrivastine has not been linked to instances of clinically apparent acute liver injury.
Background
Acrivastine (ak" ri vas' teen) is a second generation antihistamine (H1 receptor blocker) that is used to treat allergic symptoms associated with hay fever, seasonal allergies, urticaria, angioedema and atopic dermatitis. Acrivastine, like other second generation antihistamines, is considered to be nonsedating, and prospective studies have shown that sedation is less common with acrivastine than first generation antihistamines such as diphenhydramine. In the United States, acrivastine is available in combination with pseudoephrine (Semprex-D) as therapy of seasonal allergic rhinitis. Acrivastine has been less popular than other second generation antihistamines such as loratadine and cetirizine, probably because it requires three times a day dosing. The recommended dose in adults is 4 to 8 mg two or three times daily. Common side effects include blurred vision, dry mouth and throat, palpitations, tachycardia, abdominal distress, constipation and headache. Although considered to be a nonsedating antihistamine, acrivastine may cause mild drowsiness particularly at higher doses. Antihistamines can worsen urinary retention and glaucoma.
Hepatotoxicity
Acrivastine has not been linked to liver enzyme elevations or to instances of clinically apparent liver injury. Its relative safety may relate to its rapid metabolism and use in low dosages.
Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury).
References on the safety and potential hepatotoxicity of antihistamines are given together after the Overview section on Antihistamines.
Drug Class: Antihistamines
PRODUCT INFORMATION
REPRESENTATIVE TRADE NAMES
Acrivastine (with Pseudoephrine) – Semprex-D®
DRUG CLASS
Antihistamines
Product labeling at DailyMed, National Library of Medicine, NIH
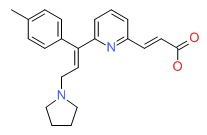
CHEMICAL FORMULA AND STRUCTURE
| DRUG | CAS REGISTRY NUMBER | MOLECULAR FORMULA | STRUCTURE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acrivastine | 87848-99-5 | C22-H24-N2-O2 |
 |
- Review Acrivastine in allergic rhinitis: a review of clinical experience.[J Int Med Res. 1989]Review Acrivastine in allergic rhinitis: a review of clinical experience.Bojkowski CJ, Gibbs TG, Hellstern KH, Major EW, Mullinger B. J Int Med Res. 1989; 17 Suppl 2:54B-68B.
- Prolonged treatment with acrivastine for seasonal allergic rhinitis.[J Int Med Res. 1989]Prolonged treatment with acrivastine for seasonal allergic rhinitis.Bruno G, D'Amato G, Del Giacco GS, Locci F, Gale NM, Errigo E, Melillo G. J Int Med Res. 1989; 17 Suppl 2:40B-46B.
- Review Acrivastine. A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy in allergic rhinitis, urticaria and related disorders.[Drugs. 1991]Review Acrivastine. A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy in allergic rhinitis, urticaria and related disorders.Brogden RN, McTavish D. Drugs. 1991 Jun; 41(6):927-40.
- Efficacy of acrivastine plus pseudoephedrine for symptomatic relief of seasonal allergic rhinitis due to mountain cedar.[Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1996]Efficacy of acrivastine plus pseudoephedrine for symptomatic relief of seasonal allergic rhinitis due to mountain cedar.Williams BO, Hull H, McSorley P, Frosolono MF, Sanders RL. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1996 May; 76(5):432-8.
- Acrivastine in two doses compared with placebo in a multicentre, parallel group study for the treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis.[Br J Clin Pract. 1989]Acrivastine in two doses compared with placebo in a multicentre, parallel group study for the treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis.Gibbs TG, McDonnell KA, Stokes T, Graham AA. Br J Clin Pract. 1989 Jan; 43(1):11-4.
- Acrivastine - LiverToxAcrivastine - LiverTox
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...