How to submit information in the Methodology section of the submission form
Strategy
To make your test more discoverable, we strongly recommend being as specific as possible in specifying what your test measures (Test targets - genes, chromosomes, proteins and analytes). For example, rather than providing free text about all the alleles or all the analytes being tested, submit each separately in the test targets section. Then use the Test comment section to describe how the combination of the specific targets is evaluated. GTR users will then be able to find your test by searching on specific genes, variants, analytes, etc. and NCBI resources such as ClinVar and MedGen will make more effective linkages to your submitted information.
Organization of this page
This page is organized according to the sections you see on the Methodology tab. You may click on the name of the section below to navigate to that section of this document.
Please note that most sections in the form provide tool tips, accessible by this icon (![]() ), that provide hints specific to that area.
), that provide hints specific to that area.
Test Method(s)
This section organizes specific fields into blocks to capture the hierarchies among methodologies and to enable the description of complex tests. Major method category, Method category, Primary Test Methodology and Instruments are grouped and numbered. You may 'add another method' if more than one group is desired or you may remove a section. Information in the Test Methods section will display in the Methodology tab of the test record.
Major method category (minimal). Choose a higher level method category from the list: Biochemical, Cytogenetic, or Molecular.
Method category (minimal). Select the general category to which the method belongs.
Choices within Biochemical:
Analyte
Enzyme assay
Immunohistochemistry
Protein analysis
Protein expression
Choices within Cytogenetics:
FISH-metaphase
FISH-interphase
Chromosome breakage studies
Sister chromatid exchange
Chromosome Rearrangement
Multicolor FISH (M-FISH)/Spectral Karyotyping™ (SKY™)
Choices within Molecular:
Deletion/duplication analysis
Detection of homozygosity
Linkage analysis
Methylation analysis
Microsatellite instability testing (MSI)
Mutation scanning of select exons
Mutation scanning of the entire coding region
Sequence analysis of select exons
Sequence analysis of the entire coding region
Targeted mutation analysis
Uniparental disomy study (UPD)
Primary Test Methodology (minimal). Provide name of the test method used in the assay e.g., RT-PCR with gel analysis, Metabolite levels, or specify a method not listed.
Instruments (recommended). Name the instrument used for a specific methodology e.g., Roche LightCycler 480, IlluminaHiSeq™2000 system, or specify an instrument not listed. Field is optional for research tests.
Platforms (optional). Select the name of a platform containing pre-defined test targets to provide methodology details and help GTR users find your test. If you use a platform not on the list, choose ‘Other’ and then provide the name. A platform name typically corresponds to a unique catalogue number or a set of catalogue numbers which are bundled with other consumables. The format is usually manufacturer name, product name, and general specifications. Field is optional for research tests.
Test procedure or protocol (optional). Summarize the methodology and describe the specific steps for each method of the assay.
Citations for test procedure or protocol (optional). Provide citations or URL for the protocol.
Confirmation of test results (recommended). Describe whether and how test results are confirmed (beyond initial validation of the assay). For example, 'Positive results are confirmed on a new DNA preparation using repeat sequence analysis'.
NOTE about research tests: Field is optional. State whether or not participants have an opportunity to learn about the results of the research test. If so, describe how participants may find out the test results, whether confirmation may be done in a clinical (e.g. CLIA-certified) lab, and whether or not there may be associated costs.
Test comment(s) (optional). Provide textual description of the test methods or any other information about your test not described elsewhere that may be useful to clinicians ordering your test, e.g. 'Bi-directional sequencing of exons 1-5 with concurrent analysis of NP_000000.0:p.Glu234Gly'.
NOTE about research tests: Use the Test comment(s) field to describe whether or not there a cost to participate in the study and if so, provide details.
NOTE we strongly encourage you to describe the test target(s) your test interrogates in the "Test Targets" section. For the example above, you would follow these steps:
- select 'gene' from the drop down menu for 'target is identified by',
- start typing the gene symbol and select the correct gene from the autocomplete dictionary,
- click the radio button for 'Associated reference sequences and exons',
- start typing the RefSeq accession and select the correct Refseq from the autocomplete dictionary
- enter the exons
- click the radio button for Variants
- start typing the HGVS expression for a tested variation, beginning with the RefSeq accession (ex. NM or NP),
- select one of the suggestions from the autocomplete dictionary or enter NM_000208.2:c.3079C>T
- click on 'Save target' to save your data
By being specific, rather than writing free text, you make it possible for us to link your test to other resources at NCBI, such as variaton-related reports and ClinVar. This will ensure your test is more readily discoverable by all users of NCBI databases.
Test Targets
Section to describe the analytes, chromosomal or mitochondrial regions, genes and variations, or proteins that are measured in the test. Use the 'Target is associated with' section to match each target with at least one condition. The test must have at least one explicit condition-target relationship.
Note the warning about the need to add at least one test target for every test, and to have at least one explicit condition-target relationship. Click ‘Add Test Target’ to open that section of the Methodology page.
Use the Test target section to enter targets (genes must be entered one at a time). Decide which specific target you are going to enter. For each target, you can provide:
- the type (germline, somatic or both) in ‘Target is’ section
- the associated condition(s) that this target evaluates in ‘Target is associated with’ section
- category (analyte, chromosomal region/mitochondrion, gene, protein) in ‘Target is identified by’ section
As an example, below are the steps to enter JAG1 for Alagille syndrome 1 and NOTCH2 for Alagille syndrome 2.
Target is (recommended). Select a radio button to indicate the type of target: germline, somatic, or both. Please note that germline is selected by default.
Target is associated with (recommended). Check one or more boxes for the indication(s) that are evaluated by the test target. In this case, Alagille syndrome 1 is associated with the JAG1 gene and Alagille syndrome 2 is associated with the NOTCH2 gene. For this example, check the Alagille syndrome 1 box.
Target is identified by (minimal). Choose 'analyte', 'chromosomal region/mitochondrion', 'gene' or 'protein'. Then specify target(s) tested in field that appears below it (which is dependent on the selection made). In this example, for ‘Target is identified by’ choose ‘gene’.
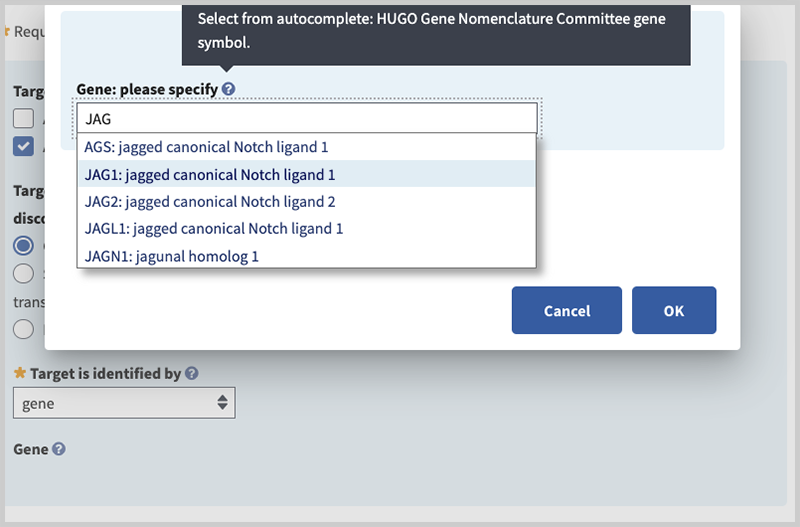
Gene: please specify (minimal if 'gene' is selected in 'Target is identified by' field). Begin typing in the box to activate autocomplete dictionary and select the desired term. Then select radio button for 'Associated Reference Sequences and Exons', 'Variants', or 'None'. The first two radio buttons activate fields to provide additional details. In this example, specify the gene in the pop-up window by typing JAG1 and selecting your choice.
Associated Reference Sequence (minimal if 'Associated Reference Sequence and Exons' selected, otherwise optional). Activate autocomplete dictionary by typing NG or NM or NC to specify the accession and version (e.g. NM_0000001.1) of the sequence used to define the test or test region. Note, NC is applicable only to genes on the mitochondrion.
NOTE: If gene name is provided, the chromosomal location will be automatically provided and does not need to be entered.
Relevant exons for each associated reference sequence (minimal if 'Associated Reference Sequence and Exons' selected, otherwise optional). We encourage the following conventions for reporting the exons being tested:
| What is tested | How to report |
|---|---|
| If a continuous range is tested |
Provide the exon numbers as a range, e.g. 2-5. If the range includes all exons, add (All), e.g. 1-5 (All) |
| If a subset is tested | Enumerate the exons tested. Ranges are allowed, e.g. 3,5,9-12 |
Clinical significance of variant (recommended if 'Variants' selected). Options are:
association
confers sensitivity
drug response
no known pathogenicity
not provided
other
pathogenic
probably not pathogenic
probably pathogenic
risk factor
variant of unknown significance
Citations to support the clinical significance (recommended). Provide citations or URL.
Then ‘Save target’. Your have now completed a target entry (the JAG1 gene) for Alagille syndrome 1.
Complete your work by clicking ‘Add Test Target’ again in order to specify the NOTCH2 gene for Alagille syndrome 2. Specify whether the target is germline, somatic or both. In this example, uncheck Alagille syndrome 1 and check Alagille syndrome 2 to prepare for entering the gene NOTCH2. For ‘Target is identified by’ choose ‘gene’, then specify in the pop-up window by typing NOTCH2 and selecting your choice. Save Target.
Analyte: please specify (minimal if 'analyte' is selected in 'Target is identified by' field). Begin typing in box to activate autocomplete dictionary, then select desired term. For example, type 'br' and select the analyte 'Branched-chain amino acids' or the enzyme 'Branched-chain ketoacid dehydrogenase'. Use 'Add another analyte' link to add multiple analytes.
Chromosomal region/mitochondrion: please specify (optional; minimal if gene name or analyte not provided). Identify chromosome or chromosome location as precisely as possible. If individual chromosomes are evaluated, enter each one as a distinct target. Use the term 'Complete genome' for comprehensive chromosomal or genomic assessments such as karyotyping, cytogenomic arrays, whole genome sequencing or chromosome breakage analysis.
When identifying a chromosome, begin typing in box 'Chromosome...' to activate autocomplete dictionary and select the desired term from the list that displays. If the desired chromosome is not listed, enter 'Chromosome [number]' in the text box and click the Save button at the bottom of the page.
When identifying a chromosomal region or band, begin typing to activate autocomplete dictionary and select the desired term from the list that displays. For example, enter chromosomal region '11p15' or range '15q11-q13'. If the desired chromosomal region is not listed, enter it in the text box. Click the Save button at the bottom of the page.
GTR uses the same formatting conventions for chromosomal band as HGNC, OMIM and NCBI's Gene. When identifying a cytogenetic band, please represent it in the p-q order and do not repeat the chromosome number. Examples: 22q11.3-q11.4 or 5p15.33-p.15.2.
When your test target is the complete mitochondrial genome, begin typing in box 'mitochondrion'. If the condition is known to result from variants in the mitochondrion, then the choice 'mitochondrion' will appear in the list that displays. (If the condition is not stored in GTR's database as being mitochondrial in origin, 'mitochondrion' will not display so you should enter 'mitochondrion' explicitly.)
NOTE: If you are testing specific mitochondrial genes, please select 'gene' in the Target is identified by section and select the genes by entering the beginning part of the gene symbol, namely MT-.
If gene name is provided, the chromosomal location will be automatically provided and does not need to be entered.
Protein: please specify (minimal if 'protein' is selected in 'Target is identified by' field). Begin typing in box to activate autocomplete dictionary and select the desired term. Add another protein as needed.
Save your work
Don't forget to save your work by clicking the Save & Continue button at the bottom of the page! If you need to interrupt or delay data entry, you can return at a later time and you will be taken to the last tab you saved.
If any required fields or data inconsistencies are detected on this page, an error message will display after you click Save & Continue indicating what the issue is. The field(s) that need attention will be outlined in red. Please correct your data and click "Save & Continue" again.







